Introduction
In the dynamic world of digital marketing and customer relationship management (CRM), the phasing out of third-party cookies represents a major turning point.
This comprehensive guide aims to dissect this important change, exploring in depth its impact on marketing and CRM strategies. We'll discuss how this evolution affects data collection and analysis, online advertising, and the personalization of customer interactions.
The aim of this guide is to provide a holistic view of the challenges and opportunities that arise, as well as to propose adaptive and innovative strategies for successfully navigating this new landscape.
Whether you're a seasoned digital marketing professional or new to the field, this guide aims to equip you with the knowledge and skills needed to excel in a world increasingly focused on privacy and protection of user data.
Historical and Current Context

History of the Use of Cookies in Marketing
What is a Cookie and How Does it Work?
A cookie is a small text file that a website sends to the user's browser. It is used to store information about the user's visits, such as browsing preferences and history. Cookies play a crucial role in personalizing and improving the online user experience.
Pixels and Tracking Codes
Google Ads pixels, Facebook Ads, and Google Analytics tracking codes are typical examples of the use of cookies in marketing. These tools track user actions on a site, collect data to analyze user behavior, and improve the effectiveness of advertising campaigns.
Heat Maps, Objectives and Utilities
Heat maps use data collected via cookies to show where users click most on a site, helping to understand their behavior. The purposes of cookies in marketing include personalizing ads, measuring campaign effectiveness, and optimizing websites for a better user experience.
Reasons for Eliminating Cookies
Privacy Concerns
With growing awareness of the importance of online privacy, cookies are increasingly seen as intrusive. Users are concerned about how their data is collected and used.
Regulations
Laws such as Bill 25 in Quebec, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States, have been put in place to protect privacy user data. These regulations limit the use of cookies and strengthen user consent requirements.
Immediate Consequences for Digital Marketing and CRM
Data Retention and Transfer Process
Businesses must now adopt strategies to retain and transfer customer data in a manner that complies with new data protection laws.
Contingency Plan
Organizations are being forced to develop contingency plans to manage changes in data collection and customer engagement without relying on cookies.
Data Management and Respect for Privacy
Digital marketing and CRM must adapt to respect user privacy while finding new methods to collect valuable data, requiring a more ethical and transparent approach to data management.
Implications for Digital Marketing Strategies
Impact on Advertising Targeting and Content Strategies
Changes in Advertising Targeting
The elimination of third-party cookies radically changes ad targeting methods. Businesses must now rely more on first-party data to target their ads. This involves a shift towards approaches based on data collected directly from customers, such as email registrations and website interactions.
Adaptation of Content Strategies
Without the detailed insights provided by third-party cookies, content strategies must become more intuitive and based on a deep understanding of the target audience. This includes creating content that truly resonates with users' interests and needs, drawing on behavioral data and direct feedback.
Necessary Adaptations for Businesses
Automation of Simple and Recurring Tasks
In a context where the workforce is increasingly limited, automation becomes crucial. Businesses can automate repetitive marketing tasks like sending emails, posting on social media, and segmenting customers. This frees up time for more strategic and creative tasks.
More Personalized Marketing
Increased use of first-party data encourages more personalized marketing. Businesses can create more relevant and engaging experiences for customers, based on real user behavior and preferences data.
Importance of an Internal Database
Having a robust internal database has become essential. This database should include detailed information about contacts, transactions, companies, customers, prospects, etc. This data provides a better understanding of the customer journey and needs, which is crucial for developing effective marketing strategies.
Automation in the Service of Time and Money
Work for You
Automation can play a significant role in working “for” the business. By automating processes, businesses can reduce costs, increase efficiency and focus on higher value initiatives.
Savings Time and Money
Automation provides significant savings in terms of time and money. By reducing the need for labor for repetitive tasks and improving the efficiency of marketing processes, businesses can allocate their resources more strategically.
In conclusion, adapting to changes in the third-party cookie landscape requires an innovative and flexible approach to digital marketing. By focusing on automation, personalization and the strategic use of first-party data, businesses can not only comply with new regulations, but also discover new opportunities to engage and retain their customer base.
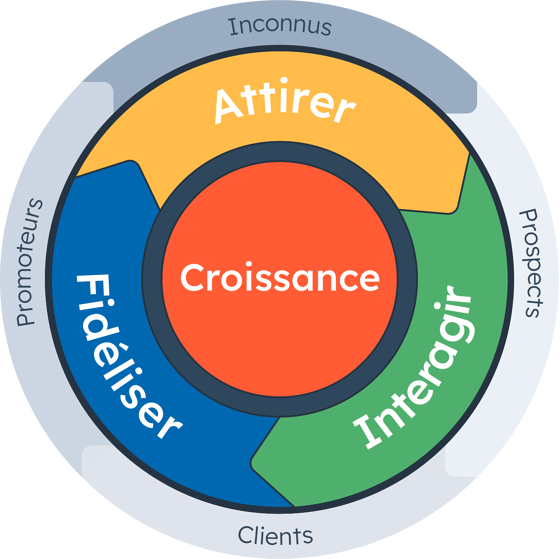
Customer Interaction and Social Media: Beyond Cookies
Algorithmic Operation of Social Platforms
Each social platform uses a unique algorithm to determine what content is presented to its users. These algorithms are designed to maximize engagement by displaying the most relevant content, based on past interactions, preferences and behaviors within the platform, rather than data collected via external cookies.
Analysis of Platforms and Their Use Without Cookies
TikTok
-
Role of Cookies : Minimal, focusing more on behavior within the application.
-
Algorithm : Prioritizes viral and trending content, based on user engagement.
-
Target Audience : Generally young, responsive to trends and creative content.
Facebook
-
Role of Cookies : Historically important for advertising targeting, but changing with regulatory changes.
-
Algorithm : Focuses on interactions with friends and family, as well as groups and followed pages.
-
Target Audience : Very diverse, with diverse age groups and interests.
Instagram
-
Role of Cookies : Used to target advertisements, but the focus is on internal application data.
-
Algorithm : Favors highly visual content, with an increasing importance of stories and reels.
-
Target Audience : Young and trend-oriented, with a strong interest in visuals.
LinkedIn
-
Role of Cookies : Less reliant on cookies for targeting, focusing on business connections.
-
Algorithm : Prioritizes relevant professional content and network publications.
-
Target Audience : Professionals, businesses and decision-makers.
Pinterest
-
Role of Cookies : Used mainly to improve user experience and advertising targeting.
-
Algorithm : Highlights visual content based on the user's interests and past interactions.
-
Target Audience : Mainly female, interested in fashion, decoration, and DIY.
Strategic Use of Social Media
Influencer Marketing and UGC
Influencer marketing and user-generated content (UGC) are two key strategies in a cookie-free world. Influencers can provide significant organic reach, and UGC can improve trust and engagement.
Adaptation to Algorithms
Understanding and adapting to social platform algorithms is essential to maximizing visibility and engagement. This includes creating relevant and engaging content, tailored to the specifics of each platform.
In conclusion, although social media uses cookies for certain functions, its primary role in customer engagement relies on interactions within the platforms and user-generated data. With privacy regulations evolving, brands must adapt by leveraging the unique capabilities of each social network to engage their audiences in a meaningful and compliant way.
International Comparative Analysis

Various Approaches to the Elimination of Cookies
Overview
The approach to eliminating cookies varies significantly between countries, primarily due to cultural and regulatory differences. This section analyzes how different regions of the world are responding to these changes and adapting to an evolving digital marketing landscape.
Influence of Local Regulations
European Union
-
GDPR : The European Union, with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), has been a pioneer in strict privacy regulations. Companies operating in these countries must obtain explicit consent for the use of cookies, strongly influencing digital marketing strategies.
UNITED STATES
-
CCPA and Other State Regulations : In the United States, regulations vary from state to state, with laws like the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) imposing restrictions similar to the GDPR. However, the overall approach is generally less strict compared to the EU.
Asia
-
Diversity of Regulations : In Asia, privacy regulations vary widely. Countries like Japan have strict data protection laws, while others have more lenient approaches.
Cultural Perceptions of Online Privacy
Europe
-
High Sensitivity to Privacy : In Europe, there is a strong sensitivity towards privacy, which is reflected in the stringency of the GDPR and in consumer attitudes.
North America
-
Balancing Privacy and Convenience : In the United States and Canada, although there is growing awareness of privacy, consumers tend to balance privacy protection with the convenience of online services.
Asia
-
Diversity of Attitudes : In Asia, attitudes towards online privacy vary greatly. In some countries there is less concern for privacy, while in others, such as South Korea, data protection is taken very seriously.
Regional Particularities
Latin America
-
Increasing Regulations : Countries in Latin America are gradually developing privacy regulations, influencing local digital marketing strategies.
Middle East and Africa
-
Developing Regulations : These regions feature a mix of emerging markets with developing regulations. The approach to cookies and privacy is constantly evolving.
This comparative analysis shows that the response to eliminating cookies and managing online privacy varies significantly across the world, influenced by local regulations and cultural perceptions.
Companies operating in the field of digital marketing must therefore adopt flexible and personalized strategies for each market, taking into account regional specificities regarding privacy, data protection and regulation.
This involves a deep understanding not only of technical and legal aspects, but also of consumer attitudes and behaviors in different cultural contexts. By staying tuned to these ever-changing dynamics, marketers can develop more effective, privacy-friendly campaigns tailored to the specific needs of each market.
Data Measurement and Analysis
The Challenges of Data Collection and Analysis without Cookies
Loss of Accurate Tracking Data
With the elimination of third-party cookies, marketers face the loss of valuable data that was essential for tracking and analyzing user behavior online. This includes difficulties in tracking the user journey across different sites and measuring the effectiveness of advertising campaigns.
Data Fragmentation
Without third-party cookies, data becomes more fragmented, making it difficult to create a complete user profile. This can lead to a less accurate understanding of customer preferences and behaviors.
Innovative Solutions and Measurement Alternatives

1. First-Party Data
-
Direct Collection : First-party data, collected directly from users through interactions on your website, email registrations, or transactions, becomes crucial.
-
Use of CRMs : Customer relationship management (CRM) systems, such as HubSpot, can help centralize and analyze this data for a better understanding of the customer.
2. Cohort Analysis and Segmentation
-
Advanced Segmentation : Use cohort analysis techniques to segment users based on common behaviors or characteristics.
-
Personalization : These analytics allow for deeper personalization and more precise targeting.
3. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
-
Predictions and Modeling : AI and machine learning can be used to analyze large amounts of first-party data and predict trends or user behaviors.
-
Insights Automation : These technologies facilitate the automatic discovery of useful insights for marketing strategies.
4. Use of Proprietary Tracking Pixels
-
Custom Pixels : Develop and use proprietary tracking pixels to collect data specific to your site or application.
-
Compliance and Transparency : Ensure these methods comply with privacy regulations and are transparent to users.
5. Surveys and Direct Feedback
-
Collection of Opinions : Encourage users to share their opinions and preferences directly through surveys or feedback systems.
-
User Engagement : This can also be used to strengthen customer engagement and loyalty.
Conclusion
Marketers must adapt to a cookie-free environment by turning to alternative data sources and adopting innovative technologies for measurement and analysis. By leveraging first-party data, leveraging AI and machine learning, and using more direct and transparent data collection methods, businesses can overcome
overcome these challenges and continue to gain valuable insights about their customers. This adaptation is not only a response to technological change, but also an opportunity to deepen the understanding of customer behavior in a more ethical and privacy-friendly way. Ultimately, these approaches can lead to a more authentic and lasting customer relationship, built on trust and better knowledge of user needs and preferences.
Legal Consequences and Compliance
Legal Implications of Eliminating Cookies
*THIS DOES NOT CONSTITUTE LEGAL ADVICE IN ANY CIRCUMSTANCES, WE ADVISE YOU TO CONTACT A SPECIALIST LAWYER IN CASE OF DOUBT*
Understanding the New Regulations
With the phasing out of third-party cookies, businesses must understand and comply with a series of new data privacy regulations. Laws like GDPR in Europe, CCPA in California, and other similar regulations around the world impose strict requirements on how users' personal data is collected, stored, and used.
Non-Compliance Risks
Failure to comply with these regulations may result in serious legal consequences, including substantial fines. Beyond the financial implications, there is a real risk to the company's reputation as consumers become increasingly concerned about the protection of their personal data.
Practical Compliance Tips
1. Compliance Audit
-
Evaluate Current Practices : Conduct a comprehensive audit of data collection and processing practices to identify potential compliance gaps.
-
Expert Consultation : Consider consulting with privacy law experts for a thorough understanding of specific requirements.
2. Transparency and Consent
-
Clear Privacy Policies : Ensure that privacy policies are easy to understand and accessible for users.
-
Informed Consent : Establish mechanisms to obtain informed and verifiable consent from users for the collection and use of their data.
3. Data Security
-
Enhanced Security Measures : Adopt robust security measures to protect data against unauthorized access, breaches and loss.
-
Employee Training : Ensure regular employee training on data security and privacy best practices.
4. First Party Data Management
-
Responsible Storage and Processing : Manage first-party data responsibly, ensuring collection and use complies with applicable regulations.
-
Respond to User Requests : Be prepared to respond quickly to user requests regarding their data, including requests for deletion or modification.
5. Regulatory Monitoring
-
Continuous Update : Stay informed of changes in privacy laws and regulations to ensure continued compliance.
-
Agile Adaptation : Be prepared to quickly adapt strategies and practices in response to new regulations.
Conclusion
Compliance with privacy laws is an essential aspect of doing business in today's digital world. By taking a proactive approach and integrating compliance into all facets of their operations, businesses can not only avoid legal consequences but also build trust
of their customers. Good data governance, increased transparency and enhanced security are fundamental pillars for successfully navigating this ever-changing regulatory landscape. Ultimately, by adopting these best practices, businesses can not only meet legal requirements, but also position privacy and responsible data management as essential competitive assets in their relationship with customers.
Consumer Perspective
Consumer Perceptions of Privacy
Growing Privacy Awareness
With the increase in discussions around data protection and privacy, consumers are becoming more aware of how their personal data is used. This increased awareness has led to a growing demand for transparency and control over how personal information is collected and used.
Distrust and Concerns
There is growing distrust of companies that collect and use data without clear consent. Data breach scandals and privacy abuses have heightened consumers' concerns about the security of their personal information.

Balance between Personalization and Respect for Privacy
Personalization Expectations
On the one hand, consumers expect personalized experiences. They value relevant recommendations and content tailored to their interests and behaviors, which requires a certain level of data collection.
Privacy Requirement
On the other hand, there is a strong demand for increased privacy. Consumers want to have control over their data and be assured that their information is handled securely and ethically.
Strategies for Business
Transparency and Control
Companies must be transparent in their data collection practices and provide consumers with clear control over how their information is used. This includes easy-to-understand privacy policies and options to opt-in for or against certain uses of their data.
Informed Consent
It is crucial to ensure that consent for data collection and use is obtained ethically and in compliance with regulations. Consent must be a clear and voluntary action on the part of the consumer.
Balance and Ethical Personalization
Businesses must strike a balance between providing effective personalization and maintaining privacy. This may involve the use of first-party data collected directly and transparently from consumers.
Conclusion
The consumer perspective on privacy is a driving factor in today's digital marketing landscape. Businesses must recognize and address these concerns by carefully balancing personalization and privacy. By adopting transparent and responsible practices, they can not only comply with regulations, but also gain consumer trust and loyalty, which is essential in an increasingly data protection-focused business environment.
Role of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning

Using AI for Personalization without Cookies
AI-Driven Personalization
With reliance on cookies decreasing, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are emerging as powerful tools for personalization. They enable the analysis of complex and large data sets to identify user trends, preferences and behaviors, providing deep personalization without relying on third-party cookies.
Behavioral and Predictive Understanding
AI can examine users' interactions with a website, their purchase histories, their responses to previous campaigns, and other first-party data to create detailed user profiles. This allows for more precise segmentation and predictions about future user preferences.
Concrete Examples of Application of AI
1. Product Recommendations
-
Recommendation Systems : E-commerce platforms use AI to suggest products based on users' browsing behavior and previous purchases. This includes personalized recommendations that increase the chances of conversion.
2. Content Optimization
-
Content Personalization : Using AI to analyze first-party data and personalize the content displayed to each user, improving engagement and content relevance.
3. Predictive Analysis
-
Predicting Trends : AI is able to predict future trends and consumer behaviors by analyzing available data, allowing businesses to anticipate market needs and adjust their strategies accordingly.
4. Chatbots and Virtual Assistance
-
Enhanced Customer Service : AI-powered chatbots provide instant, personalized customer support. They can answer questions, suggest products and even resolve issues, providing an improved customer experience.
5. Targeted Advertising
-
Precise Targeting without Cookies : Using AI for ad targeting allows businesses to target audiences more precisely, leveraging first-party data and behavioral analytics.
Conclusion
AI and Machine Learning play a vital role in the post-cookie era, enabling advanced personalization and targeted marketing without relying on third-party cookies. Their ability to analyze massive volumes of first-party data and derive precise insights opens new avenues for more relevant and engaging customer interaction. By adopting these technologies, businesses can not only
staying at the forefront of innovation, but also offering enriched user experiences, thus increasing customer satisfaction and promoting loyalty. AI and ML are not just alternatives to cookies; they represent an evolution towards smarter, responsible and customer-centric marketing practices.
Impact on Small vs. Large Businesses
Impact Differences and Adaptive Strategies
Impact on Small Businesses
-
Limited Resources : Small businesses, with limited budgets and resources, may find it more difficult to adapt to changes and invest in new technologies.
-
Flexibility and Agility : However, their smaller size can allow greater flexibility and faster adaptation to new strategies.
Impact on Large Businesses
-
Higher Resource Capabilities : Larger companies generally have more resources to invest in advanced technologies like AI and Machine Learning.
-
Integration Challenges : However, they may face challenges in integrating new solutions across large and complex organizational structures.
Effects on Programmatic Advertising and Real-Time Bidding
Programmatic Advertising
-
Reduced Reliance on Third-Party Cookies : Businesses must find new ways to target audiences effectively without relying on third-party cookies.
-
Use of First-Party Data : The focus is on using first-party data and AI-based solutions for segmentation and targeting.
Real-Time Bidding
-
Changes in Bidding Strategies : Real-time bidding strategies must adapt to use alternative data, such as first-party contextual and behavioral data.
Importance of the Multichannel and Omnichannel Approach
-
Consistency across All Channels : A multi-channel and omni-channel approach is essential to reaching consumers where they are, creating a consistent experience across all communication channels.
-
Compensating for Lost Cookies : This approach helps compensate for the loss of accurate tracking data provided by cookies.
Ethical Practices in a Cookie-Free Environment
Ethics and Transparency
-
Consent and Privacy : Companies must ensure that they obtain user consent in an ethical and transparent manner.
-
Avoiding Deceptive Practices : It is crucial to avoid any practices that may deceive users or violate privacy regulations.
Risks of Unethical Approaches
-
Sanctions and Reputation : Using unethical methods to collect and use data can result in legal sanctions and harm the company's reputation.
-
Loss of Consumer Trust : Unethical practices can also lead to a loss of consumer trust, which is difficult to regain.
Training and Education for Marketing Professionals
Stay up to date
-
Continuing Education : It is important for marketing professionals to continue their education
and training to stay up to date with the latest trends, tools, and regulations.
-
Webinars, Workshops and Certifications : Participating in webinars, workshops and obtaining relevant certifications can help acquire the skills needed in a rapidly changing marketing environment.
Online Resources
-
Access to Digital Resources : Numerous online resources, such as courses, tutorials, and industry blogs, are available to help professionals adapt to changes.
Conclusion
The impact of eliminating cookies varies between small and large businesses, with each needing to adopt adaptive strategies based on their resources and capabilities. While larger companies may have more resources to invest in advanced technologies, smaller businesses can benefit from their agility and flexibility.
The key for all businesses is adopting ethical and transparent approaches, leveraging first-party data, and engaging in multi- and omni-channel strategies. Additionally, continuing education is essential for all marketing professionals to successfully navigate this ever-changing landscape and maintain a trusted relationship with consumers.
Conclusion
Summary of Main Points
Paradigm Shift in Digital Marketing
The gradual elimination of third-party cookies marks a new era in digital marketing and CRM. This change requires businesses to re-evaluate and adapt their strategies around data collection, personalization, advertising and customer engagement.
The Importance of First Party Data
The disappearance of third-party cookies highlights the value of first-party data. Businesses must focus on collecting and ethically analyzing this data to deliver personalized and relevant customer experiences.
Growing Role of AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are emerging as key tools to fill the void left by third-party cookies. They offer advanced ways to analyze data, predict customer behaviors, and personalize interactions in more meaningful and privacy-friendly ways.
Adaptation to Constantly Changing Regulations
Compliance with data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, remains a major challenge. Businesses must be vigilant, transparent and ethical in their data management to avoid legal risks and build customer trust.
Multichannel and Omnichannel Approaches
In a world without cookies, the multichannel and omnichannel approach becomes essential. It helps create a consistent and integrated customer experience across various platforms and touchpoints.
Implications for the Future
The digital marketing landscape continues to evolve, and businesses must remain agile and innovative to adapt. A focus on privacy and data protection opens new avenues for more authentic and respectful interactions with customers.
Invitation to Reflection and Strategic Adaptation
This changing environment offers a unique opportunity for businesses to rethink their marketing strategies. Staying informed, quickly adapting to changes, and leveraging new technologies and methods is essential to staying competitive. Marketing professionals are urged to embrace these changes, innovate and evolve, always putting customer interests and privacy at the forefront of their strategies. By doing this, businesses can not only comply with the new standards but also forge stronger, more lasting relationships with their customers.